Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.3
Question 1.
Solve the following pair of linear equations by the substitution method,
(i) x + y = 14, x – y = 4
(ii) s – t = 3, s/3 + t/2 = 6
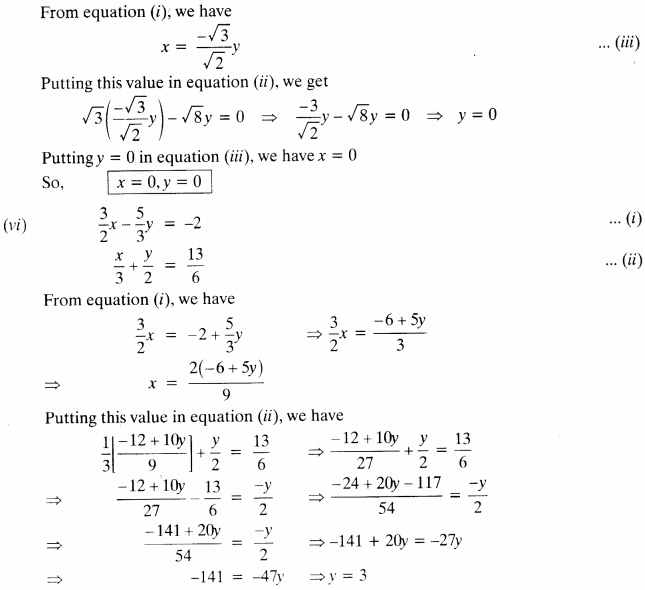
(iii) 3x – y = 3, 9x – 3y = 9
(iv) 0.2x + 0.3y = 1.3, 0.4x + 0.5y = 2.3
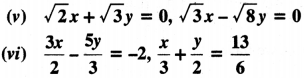
Solution:
From equation (i),
x + y – 14 ⇒ y = 14x
Putting the value ofy in equation (ii), we get
x – (14 – x) = 4 ⇒ x – 14 + x = 4 ⇒ 2x = 4 + 14
2x = 18 ⇒ x = 9
Now, puttingx = 9 in equation (i), we have
9 + y = 14 ⇒ y = 14 – 9 ⇒ y = 5
so, x = 9, y = 5
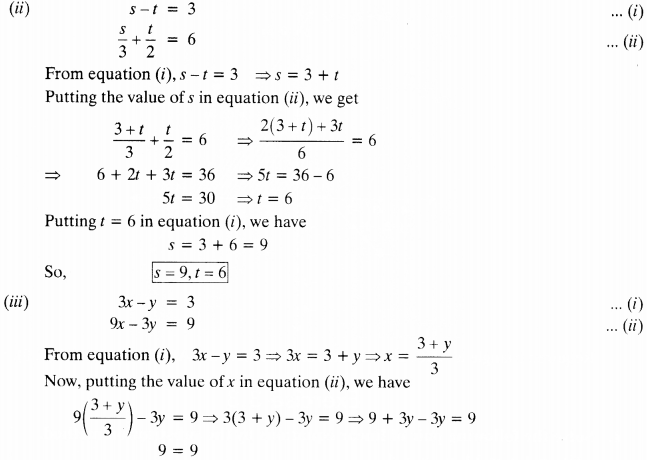
∴ y can have infinite real values
∴ x can have infinite real values because x = y+33

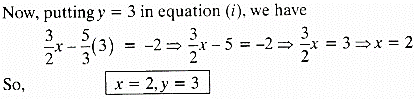
Question 2.
Solve 2x + 3y = 11 and 2x – 4y = – 24 and hence find the value of ‘m’ for which y = mx + 3.
Solution:

Question 3.
Form the pair of linear equations for the following problems and find their solution by substitution method.
(i) The difference between two numbers is 26 and one number is three times the other. Find them.
(ii) The larger of two supplementary angles exceeds the smaller by 18 degrees. Find them.
(iii) The coach of a cricket team buys 7 bats and 6 balls for ₹ 3800. Later, she buys 3 bats and 5 balls for ₹ 1750. Find the cost of each bat and each ball,
(iv) The taxi charges in a city consist of a fixed charge together with the charge for the distance covered. For a distance of 10 km, the charge paid is ₹ 105 and for a journey of 15 km, the charge paid is ₹ 155. What are the fixed charges and the charge per km₹ How much does a person have to pay for travelling a distance of 25 km₹
(v) A fraction becomes 9/2, if 2 is added to both the numerator and the denominator. If, 3 is added to both the numerator and denominator it becomes 5/6, Find the fraction.
(vi) Five years hence, the age of Jacob will be three times that of his son. Five years ago, Jacob’s age was seven times that of his son. What are their present ages?
Solution:
(i) Let 1st number be x and 2nd number be y.
Let x >y
1st condition :
x – y = 26
2nd condition :
x = 3y
Putting x = 3y in equation (i)
3y – y = 26 ⇒ 2y = 26 ⇒ y = 13
From (ii)
x = 3 x 13 = 39
∴ One number is 13 and the other number is 39.
(ii) Let one angle be x and its supplementary angle = y
Let x > y
1st Condition :
x + y = 180°
2nd Condition :
x – y = 18° ⇒ X = 18° + y
From equation (ii), putting the value ofx in equation (i),
18° + y + y = 180° ⇒ 18° + 2y = 180°
2y = 162° ⇒ y = 81°
From (ii) x = 18° + 81° = 99° ⇒ x = 99°
∴ One angle is 81° and another angle is 99°.
(iii) Let cost of 1 bat = ₹x and cost of 1 ball = ₹y
1st Condition:
7x + 6y = 3800
2nd Condition:
3x + 5y = 1750
From equation (ii), we get
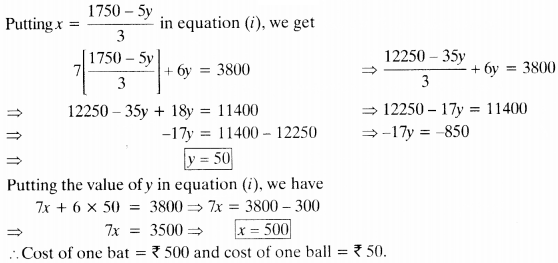
putting x = 1750-5y/3 in equation (i), we get
Cost of one bat = ₹ 500 and cost of one ball = ₹ 50.
(iv) Let fixed charges be ₹.v and charge for per km be ₹y.
A.T.Q.
1st Condition :
x + lOy = 105
2nd Condition :
x + 15y = 155
From equation (i), we get
x= 105 – 10y
Putting this value in equation (ii), we have
105 – 10y + 15y = 155 ⇒ 105 + 5y = 155
⇒ 5y = 155 – 105 ⇒ 5y = 50 ⇒ y = 10
Now, puttingy = 10 in equation (i), we have
x + 10(10) = 105 ⇒ x + 100 = 105 ⇒ x = 5
Fixed charges is ₹ 5 and charges per km is ₹ 10.
3rd Condition :
For distance of 25 km
x + 25y = 5 + 25(10) = 5 + 250 = 255
Amount paid for travelling 25 km is ₹ 255.
(v) Let numerator be x and denominator be y.
∴ Fraction is x/y
A.T.Q.
1st condition :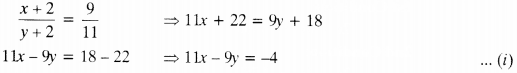
2nd condition :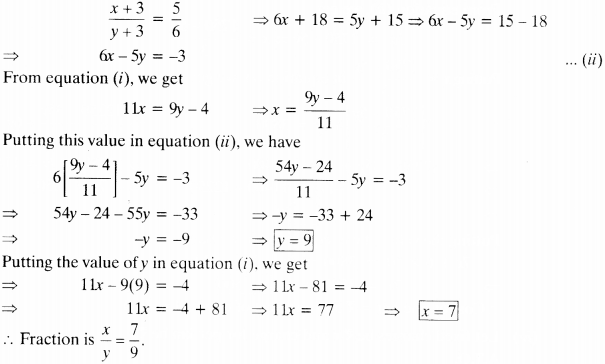
(vi) Let present age of Jacob be x years and that of his son bey years.
A.T.Q.
1st Condition :
x + 5 = 3(y + 5) ⇒ x + 5 = 3y + 15 ⇒ x – 3y = 15 – 5 ⇒ x – 3y = 10
2nd Condition:
x – 5 = 7(y – 5) ⇒ x – 5 = 7y – 35 ⇒ x = 7y – 35 + 5
⇒ x = 7y – 30
Putting the value of ‘x’ in equation (i), we get
7y – 30 – 3y = 10
4y – 30 = 10
4y = 40 y = 10 ⇒ y = 10
putting the value of y in equation(ii), we get
x = 7(10) – 30 = 70 – 30 ⇒ x = 40
Hence, the present age of Jacob is 40 years and that of his son is 10 years.