1 Grammar Tenses
Time (समय अथवा काल) किसी विशेष भाषा द्वारा संचालित नहीं है, यह तो मानव की कल्पना है . व मानव ने समय या काल को तीन भागों में विभाजित किया है
I. Present Tense — वर्तमान काल
II. Past Tense — भूत काल
III. Future Tense — भविष्यत् काल
Tenses का उपवर्गीकरण-प्रत्येक Tense को 4-4 Tenses में पुनः वर्गीकृत किया गया है
1. Indefinite or Simple
2. Continuous or Progressive
3. Perfect तथा
4. Perfect Continuous.
इस प्रकार कुल 12 Tenses हुए, जिनका यहाँ संक्षिप्त विवरण, उनके GOLDEN RULES तथा उनके सूत्र (Formulas) दिए जा रहे हैं।
1. Present Indefinite Tense
or
Simple Present Tense
आशय-वे Verbs अथवा वाक्य जिनसे वर्तमान समय में काम होना प्रकट हो (परन्तु verb से निश्चित समय का बोध न हो), Present Indefinite Tense अथवा Simple Present Tense कहलाते हैं।
Present Indefinite Tense की पहचान-हिन्दी में ऐसे वाक्यों में क्रिया के अन्त में प्रायः -ता है, ती है, ते हैं, ता हूँ शब्द आते हैं।
Golden Rule : 1 : I, We, You, They तथा Plural Nouns (जैसे – boys, teachers आदि) के साथ verb की I Form आती है।
Golden Rule : 2 : He, She, It तथा Singular Nouns (जैसे – मुकेश, बबीता-आदि ये वास्तव में III Person Singular हैं) के साथ verb की I Form + -s या – es का प्रयोग करते हैं।
सूत्र (Formula)-S + verb की I Form…..
Example:
1. मैं जाता हूँ। — I go.
2. हम पढ़ते हैं। — We read.
3. तुम दौड़ते हो। — You run.
4. वे स्कूल जाते हैं। — They go to school.
5. बच्चे खेलते हैं। — Children play.
6. वह सोता है। — He sleeps.
7. रानी भोजन पकाती है। — Rani cooks food.
8. यह लड़का एक मेज बनाता है। — This boy makes a table.
Golden Rule : 3 :
Negative (नकारात्मक) वाक्यों में I, We, You, They तथा Plural Noun के साथ –do not + verb की I Form का प्रयोग कीजिये। किन्तु he, she, it तथा Singular Noun के साथ –does not + verb की I Form का प्रयोग करो।
सूत्र (Formula)-Sub. + do/does + not + V1…..
Examples
1. तुम नहीं दौड़ते हो। — You do not run.
2. मैं नहीं खेलता हूँ। — I do not play.
3. हम नहीं सोते हैं। — We do not sleep.
4. लड़के स्कूल नहीं जाते हैं। — Boys do not go to school.
5. बच्चे नहीं रोते हैं। — Children do not weep.
6. वह नहीं लिखता है। — He does not write.
7. सविता भोजन नहीं पकाती है। — Savita does not cook food.
8. यह लड़का एक मेज नहीं बनाता है। — This boy does not make a table.
Golden Rule : 4 : (a) :
Interrogative Sentences (प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य) जो ‘क्या’ से आरम्भ होते हैं – ऐसे वाक्यों का अनुवाद करते समय I, We, You, They तथा Plural Noun के पहले .. Do रखो अर्थात् ऐसे वाक्य Do से आरम्भ करो, और अन्त में प्रश्नवाचक चिह्न (?) लगाओ। किन्तु He, She, It तथा Singular Noun के साथ Does का प्रयोग करो, अर्थात् ऐसे वाक्य Does से आरम्भ करो और वाक्य के अन्त में प्रश्नवाचक चिह्न (?) लगाओ। सूत्र (Formula)-Do/Does + Sub. + V1 ……………. ?
Examples
1. क्या तुम दौड़ते हो? — Do you run?
2. क्या मैं खेलता हूँ? — Do I play?
3. क्या हम सोते हैं? — Do we sleep?
4. क्या लड़के स्कूल जाते हैं? — Do the boys go to school?
5. क्या बच्चे हँसते हैं? — Do the children laugh?.
6. क्या वह लिखता है? — Does he write?
7. क्या सविता भोजन पकाती है? — Does Savita cook food?
8. क्या यह लड़का एक मेज बनाता है? — Does this boy make a table?
Golden Rule : 4 : (b) :
वाक्य के बीच में यदि Question word (प्रश्नसूचक शब्द) हो (जैसे – क्या, कहाँ, कब, कौन, कैसे) तो Question word (जैसे-What, Where, When, How आदि) से वाक्य आरम्भ होगा; और उसके पश्चात् नियमानुसार do, does, helping verb आयेगा, फिर शेष वाक्य का अनुवाद होता है। जैसेसूत्र (Formula)-Wh – + do/does + sub. +V1 ……………?
Examples
1. तुम क्या खेलते हो? — What do you play?
2. वह क्या लिखता है? — What does he write?
3. तुम.कहाँ रहते हो? — Where do you live?
4. सीता कहाँ रहती है? — Where does Sita live?
5. तुम कब सोते हो? — When do you sleep?
6. बबीता कब सोती है? — When does Babita sleep?
7. मैं कैसे बोलता हूँ? — How do I speak?
8. वह कैसे गाती है? — How does she sing?
9. वे क्यों रोते हैं? — Why do they weep?
10. वह क्यों रोती है? — Why does she weep?
विशेष ध्यान दें-ऐसे वाक्यों में Who के साथ do अथवा does का प्रयोग नहीं होता है। (लेकिन negative वाक्यों में Who के साथ आवश्यकतानुसार do या does आता है।)
Examples
1. कौन दौड़ता है? — Who runs?
2. तुम्हें कौन जानता है? — Who knows you?
3. मेज को कौन बनाता है? — Who makes a table?
Interrogative-Negative Sentences बनाते समय मुख्य verb के पहले ‘not’ लगाओ। जैसे
Examples
1. क्या तुम नहीं दौड़ते हो? — Do you not run?
2. क्या मैं नहीं खेलता हूँ? — Do I not play?
3. क्या वह नहीं सोता है? — Does he not sleep?
4. क्या सविता भोजन नहीं पकाती है? — Does Savita not cook food?
5. कौन पत्र नहीं लिखता है? — Who does not write a letter?
प्रयोग (Uses)
1. Present Indefinite Tense का प्रयोग आदतन क्रिया (habitual activity) को व्यक्त करने हेतू भी किया जाता है। इस कारण इस Tense में क्रिया की बारंबारता अथवा दुर्लभता दर्शाने हेतु क्रिया-विशेषण (Adverb) अथवा क्रिया-विशेषण अभिव्यक्ति (Phrase) का प्रयोग किया जाता है,
जैसे – often, always, rarely, every week/day/month/year, sometimes, occasionally, on Mondays, twice a day/week/month/year आदि।
She occasionally watches a movie.
The doctor visits the patient everyday.
2. इस Tense का प्रयोग शाश्वत सत्य (Universal Truths) को प्रकट करने हेतु भी किया जाता है
Two and two make four.
The earth moves round the sun.
3. सीमित क्रियाओं के साथ इसका प्रयोग पूर्व-निर्धारित निकट भविष्य में होने वाले कार्यों के लिए भी होता है
The Prime Minister leaves next week for the U.S.A.
My father retires next month.
4. Newspaper headlines में भी इसका प्रयोग किया जाता है
The President reaches England.
The opposition supports the motion.
5. भूतकाल की घटनाओं के वर्णन को रोचक एवं सजीव बनाने हेतु भी इस Tense का प्रयोग किया जाता है
India wins freedom in 1947.
Pratap lifts his sword and strikes at the enemy.
6. मैचं (Matches) की कमेन्ट्री में भी इसका प्रयोग किया जाता है
Dhoni aims at the ball, hits it strongly, makes two runs, ……etc.
7. किसी प्रयोग (experiment) अथवा प्रक्रिया को दर्शाने हेतु भी इसका प्रयोग किया जाता है।
I take some water in a cup, put a little salt in it, stir the water with a spsoon……etc.
8. जन्मजात गुणों के साथ (with inherent qualities)
Two enemies hate each other.
Parents look after their children.
9. वैज्ञानिक या आध्यात्मिक या अन्य सिद्धांतों के (with scientific or spiritual or other principles and theories)
Oxygen helps in compustion.
Water contains hydrogen and oxygen.
10. कथन कहानतें आदि के साथ (with quotations, proverbs etc.)
Tilak says, “Freedom is my birth right.
Fortune favours the brave.
11. अवबोधात्मक क्रियाओं के साथ (With verbs of perception – notice, see, watch, feel, hear, smell, taste etc.)
I notice sadness on your face now.
This mango tastes sweet.
12. संज्ञानात्मक क्रिया ओं के साय (With verbs of cognition – know, suppose, remember, forget, believe, mean, think, understand, trust)
I trust you.
She knows my nature.
13. भावातात्मक क्रियाओं के साथ (With verbs of emotions-love, hate, anger, fear, desire, hope, ‘like, want, wish, mind, prefer)
I prefer reading books.
She fears from darkness.
14. अन्य विविध क्रियाओ के साथ (With some miscellaneous verbs-appear, seem, resemble, matter, consist of, contain, deserve)
She resembles her sister.
She deserves this post.
15. सशर्त अदेशात्मक वाक्य में (With Conditional – Impertive) –
Work hard if you want success.
Get up when the officer enters his office.
16.नकारात्मक – आदेशामक वाक्या में (With Negative-Imperative)
Don’t disturb me. Don’t pluck flowers.
Exercise 1.
Fil in the blanks with the right form of the Simple Present form of the verb :
1. Some vegetarians ……………… (eat) fish and eggs but do not eat meat.
2. Pushpa ………….. (play) hockey every weekend.
3. The Post Office ………….. (open) at 10 a.m.
4. The, Mahanadi …… (flow) into the Bay of Bengal.
5. The planets ………………….. (orbit) round the sun.
Answer:
1. eat
2. plays
3. opens
4. flows
5. orbit
2. Present Continuous Tense
Or
Present Progressive Tense
आशय-इस Tense में वर्तमान काल में कार्य का जारी रहना प्रकट होता है, किन्तु यह मालूम नहीं पड़ता कि कार्य कब प्रारम्भ हुआ और कब समाप्त होगा।
मुख्य लक्षण-इस Tense के तीन प्रमुख लक्षण हैं
1. कार्य भूतकाल में किसी समय आरम्भ हुआ था। आरम्भ होने का समय मालूम नहीं पड़ता है।
2. वह कार्य वर्तमान समय में भी चालू रहता है। दूसरे शब्दों में, जिस समय बात कही जा रही है, उस समय भी काम जारी रहता है, समाप्त नहीं होता है।
3. वह कार्य भविष्य में कभी समाप्त होगा किन्तु कब समाप्त होगा, यह मालूम नहीं पड़ता है।
पहचान – हिन्दी वाक्यों में verb (क्रिया) के अन्त में प्रायः -रहा/हुआ है,-रही/हुई है,-रहे/हुए हैं, -रहा/हुआ हूँ शब्द आते हैं। जैसे –
1. विद्यार्थी पढ़ रहे हैं।
2. सीता कमरे में सोई हुई है।
Golden Rules :
1. Subject के बाद आवश्यकतानुसार is, are या am आता है।
2. उसके बाद मुख्य verb की I Form (Present Tense) के अन्त में -ing जोड़ देते हैं।
3. इसके पश्चात् वाक्य में कोई Object आदि हो तो उसे लिखते हैं।
सूत्र (Formula) – S + is/are/am + I form + ing +……..
I के साथ am, Singular Subject के साथ is तथा Plural Subject के साथ are का प्रयोग करो। Verb में -ing लगाने के कुछ नियम —
1. यदि verb के अन्त में कोई Consonant हो तो उसके अन्त में -ing जोड़ देते हैं । जैसे – eat = eating. drink = drinking, sing = singing, bring = bringing….आदि।
2. यदि verb के अन्त में -e हो तो -e को हटा कर -ing जोड़ देते हैं। जैसे – make = making. prepare = preparing, write = writing, give = giving, take = taking, shine = shining, ride = riding…….आदि।
3. यदि किसी verb के अन्त में एक consonant हो और उसके पहले एक vowel हो (अर्थात् verb के अन्त में एक vowel तथा एक consonant), तो -ing को जोड़ने से पहले consonant को double कर दो। जैसे – cut = cutting, run = running, swim = swimming.
4. यदि verb के अन्त में consonant हो और उससे पहले एक से अधिक vowel हों तो consonant को double मत करो और -ing जोड़ दो। जैसे – beat = beating, feel = feeling, treat = treating.
Examples
1. मैं एक पत्र लिख रहा हूँ। — I am writing a letter.
2. तुम दौड़ रहे हो। — You are running.
3. हम किताबें बेच रहे हैं। — We are selling books.
4. वे टी.वी. देख रहे हैं। — They are watching T.V.
5. वह फुटबाल खेल रहा है। — He is playing football.
6. तुम कमरे में बैठे हुए हो। — You are sitting in the room.
7. सीता कमरे में सोई हुई है। — Sita is sleeping in the room.
अपवाद – 1: कुछ क्रियाएँ ऐसी होती हैं जिनका Present (तथा Past) Continuous Tense नहीं होता है। वे सदैव Simple Present (अथवा Simple Past Tense) में ही रहती हैं। ऐसी प्रमुख क्रियाएँ निम्नलिखित हैं
belong, seem, depend, equal, own, appear, deserve, matter……
2. संवेदना-सूचक कुछ क्रियाओं का Present (तथा Past) Continuous Tense नहीं होता है, उनका प्रयोग Indefinite Tense में ही होता है। ऐसी प्रमुख क्रियाएँ निम्नलिखित हैं
love, want, like, dislike, hate, desire, hope, forgive, please……etc.
Golden Rule :
Negative (नकारात्मक) वाक्यों में Helping verb (is, are, am) के बाद (किन्तु मुख्य verb के पहले) not आयेगा।
I के साथ am; we, they तथा Plural Noun के साथ are; he, she, it तथा Singular Noun के साथ is आयेगा।
सूत्र (Formula) Subject + is/are/am + not + verb की I form में -ing…..
Examples:
1. मैं नहीं खेल रहा हूँ। — I am not playing.
2. हम नहीं लिख रहे हैं। — We are not writing.
3. तुम नहीं खा रहे हो। — You are not eating.
4. वे नहीं सो रहे हैं। — They are not sleeping.
5. अध्यापक बातें नहीं कर रहे हैं। — Teachers are not talking.
6. वह गाली नहीं दे रहा है। — He is not abusing.
7. सीता गाना नहीं गा रही है। — Sita is not singing a song.
Golden Rule-‘क्या’ से प्रारम्भ होने वाले Interrogative (प्रश्नवाचक) वाक्यों में Helping Verb (is, am, are) से वाक्य आरम्भ करो। इसके बाद Subject तथा उसके बाद Verb की I Form में -ing लगाओ। सूत्र (Formula)-Is/Are/Am + Subject + Verb की I Form में -ing……..?
Examples :
1. क्या मैं खेल रहा हूँ? — Am I playing?
2. क्या हम लिख रहे हैं? — Are we writing?
3. क्या तुम खा रहे हो? — Are you eating?
4. क्या वे सो रहे हैं? — Are they sleeping?
5. क्या अध्यापक बातें कर रहे हैं? — Are the teachers talking?
6. क्या वह गाली दे रहा है? — Is he abusing?
7. क्या सीता गाना गा रही है? — Is Sita singing a song?
Golden Rule : यदि वाक्य के बीच में प्रश्नसूचक शब्द (क्या, कहाँ, कब, कौन, कैसे….आदि) होने पर वाक्य wh-word (what, where, when, who, how…….अदि) से प्रारम्भ होगा।
(i) Wh- के तुरन्त बाद Helping Verb (is, are, am) लगाओ।
(ii) H.V. के तुरन्त बाद Subject लगाओ। सूत्र (Formula)-Wh- + H.V. + Subject + V1 में -ing………..?
Examples :
1. मैं क्या खेल रहा हूँ? — What am I playing?
2. मैं कैसे खेल रहा हूँ? — How am I playing?
3. हम क्या लिख रहे हैं? — What are we writing?
4. तुम क्यों सो रहे हो? — Why are you sleeping?
5. अध्यापक क्या बातें कर रहे हैं? — What are the teachers talking?
6. वह गाली क्यों दे रहा है? — Why is he abusing?
7. सीता कौनसा गाना गा रही है? — Which song is Sita singing?
Golden Rule : Interrogative-nmegative (नकारात्मक-प्रश्नवाचक) वाक्यों में मुख्य verb के पहले not लगाओ।
सूत्र (Formula)
(i) H.V. + S + Not + V1 में -ing………..?
(ii) Wh- + H.V. + S + Not +V1 + में ing……….. ?
Examples:
1. क्या मैं नहीं खेल रहा हूँ? — I am I not playing?
2. क्या हम नहीं लिख रहे हैं? — Are we not writing?
3. क्या तुम नहीं खा रहे हो? — Are you not eating?
4. वे क्यों नहीं सो रहे हैं? — Why are they not sleeping?
5. क्या अध्यापक बातें नहीं कर रहे हैं? — Are the teachers not talking?
6. क्या वह गाली नहीं दे रहा है? — Is he not abusing?
7. क्या सीता गाना नहीं गा रही है? — Is Sita not singing a song?
प्रयोग (Uses) –
1. इस Tense का प्रयोग बोलने के समय जारी कार्यों को दर्शाने हेतु किया जाता है
I am reading a book on English.
2. अतिशीघ्र भविष्य में होने जा रहे पूर्व निर्धारित कार्यों के लिए भी इस Tense का प्रयोग किया जाता है। इस प्रयोग में भविष्य काल का क्रिया-विशेषण (Adverb अथवा Adverb phrase) भी आता है
We are planning to buy a new house next month.
Alok is leaving for Mumbai tomorrow.
3. इसका प्रयोग ऐसी क्रिया को दर्शाने हेतु भी किया जाता है जो बोलने अथवा लिखने के क्षण में न हो रही हो किन्तु एक लम्बी अवधि के दौरान होती रहती हो।
Alok is rading for an M.A. these days.
4. बारंबारता बताने वाले क्रिया-विशेषणों के प्रयोग से यह Tense आदतन क्रिया भी दर्शाता है
He is always complaining.
5. जब निम्न क्रियाएँ परिस्थिति परिवर्तन की ओर संकेत करें
(become, turn, get, go, grow, take etc.) Ice is slowly turning into water. India is gradually taking a new shape.
Exercise 2.
Fill in the blanks with correct form of the verbs of Present Progressive Tense.
1. The pilgrims ………………. (climb) the mountains at this moment.
2. A tourist …………….. (ski) on the snow at this time.
3. The police ………….. (chase) the ruffians now.
4. The Education Minister ……………. (visit) the town tomorrow.
5. The rich …………… (not help) the poor these days. . .
Answer:
1. are climbing
2. is skiing
3. are chasing (Police हमेशा बहुवचन होता है)
4. is visiting (भविष्य का नियोजित कार्य present progressive में लिख सकते हैं),
5. are not helping (the+adjective बहुवचन होता है।)
3. Present Perfect Tense
आशय-वे वाक्य जिनसे प्रकट होता है कि कार्य अभी-अभी समाप्त हुआ है अथवा कार्य कुछ समय पहले ही समाप्त हो चुका है तो वहाँ Present Perfect Tense का प्रयोग होता है। यह Tense कार्य की समाप्ति अथवा पूर्णता बतलाता है।
ध्यातव्य बिन्दु
1. यह Tense यह तो बतलाता है कि क्रिया पूरी हो चुकी है किन्तु यह नहीं बतलाता है कि क्रिया किस समय (at what time) अथवा कब (when) समाप्त हुई।
2. ध्यान दो कि इस Tense में Past Tense सूचक adverb (जैसे – yesterday, last month, last year, last week) का प्रयोग कभी नहीं होता है। पुनः ध्यान दो कि ज्योंही Past Tense सूचक adverb आता है त्यों ही वाक्य Past Tense हो जाता है, वह Present Perfect Tense नहीं रह सकता।
पहचान-
(i) ऐसे वाक्यों में हिन्दी में -चुका हूँ, -चुकी है, -चुका है, -चुके हैं शब्द अन्त में आते हैं।
(ii) ऐसे वाक्यों में क्रिया के अन्त में -1 हूँ, – 1 है, – है, – हैं आदि अक्षर आते हैं।
Golden Rule – ऐसे वाक्यों में Subject के बाद आवश्यकतानुसार has या have का प्रयोग करते हैं। और उसके बाद verb की III Form आती है।
ध्यातव्य-
1. Singular Subject (he, she, it, Sita, boy…….आदि) के साथ has का प्रयोग करो; I तथा Plural Subject (we, you, they, boys……….) के साथ have का प्रयोग करो।
2. has, have के बाद verb की III Form अवश्य आयेगी।
सूत्र (Formula)-S + has/have + verb की III form……
3. Adverb phrase का प्रयोग होता है जिसमें समय या अवधि का नाम दिया होता है
just, so far, always, never, yet since, for etc.
Examples
1. मैंने अभी एक पत्र लिखा है — I have just written a letter.
2. तुम जयपुर देख चुके हो। — You have seen Jaipur.
3. उसने सदैव भोजन पकाया है। — She has always cooked food.
4. मनीष सो चुका है। — Maneesh has slept.
5. वे इस कहानी को पढ़ चुके हैं। — They have read this story.
6. सीता ने यह कमीज धोई है। — Sita has washed this shirt.
7. विद्यार्थियों ने इस काम को पूरा किया है। — The students have finished this work.
8. अध्यापक हमें यह पाठ पढ़ा चुका है। — The teacher has taught us this lesson.
Negative Sentences-ऐसे वाक्य में has/have के बाद not का प्रयोग होता है अर्थात् verb की III form के पहले not का प्रयोग होता है। सूत्र (Formula) – S + has/have + not + verb की III form….
Examples
1. मैंने अभी पत्र नहीं लिखा है। — I have not written a letter yet.
2. मैंने एक पत्र नहीं लिखा है। — I have not written a letter.
3. तुमने जयपुर कभी नहीं देखा है। — You have never seen Jaipur.
4. उसने अभी भोजन नहीं पकाया है। — She has not cooked food yet.
5. उसने भोजन नहीं पकाया है। — She has not cooked food.
6. तुमने अभी तक आम नहीं खाया है। — You have not eaten a mango so far.
7. अध्यापक ने हमें यह पाठ कभी नहीं पढ़ाया — The teacher has never taught us this lesson.
Interrogative Sentences (प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य) :
(1) क्या से प्रारम्भ होने वाले वाक्य आवश्यकतानुसार Has अथवा DHave से प्रारम्भ होते हैं।
(2) Has अथवा Have के बाद Subject लगाओ।
(3) Subject के बाद verb की III form लगाओ। सूत्र (Formula)-Has/Have + S + verb की III form…….?
(4) वाक्य के बीच में प्रश्नसूचक शब्द (जैसे क्या, कहाँ, कब, कौन, कैसे होने पर वाक्य Question word (जैसे what, where, when, who, how…… आदि) से प्रारम्भ होगा।)
सूत्र (Formula)-Wh- + has/have + S + V की III form………..?
Examples
1. क्या मैं एक पत्र लिख चुका हूँ? — Have I written a letter?
2. क्या तुम जयपुर देख चुके हो? — Have you seen Jaipur?
3. क्या वह भोजन पका चुकी है? — Has she cooked food?
4. वह क्या पका चुकी है? — What has she cooked ?
5. उसने क्या पकाया है? — What has she cooked?
6. क्या वे दिल्ली गये हैं — Have they gone to Delhi ?
7. वे कहाँ गये हैं? — Where have they gone ?
8. तुमने यह कहानी कब पढ़ी है? — When have you read this story ?
नोट – read (पढ़ना) की तीनों form एक समान होती हैं.

Interrogative negative-(नकारात्मक प्रश्नवाचक)
इनमें मुख्य क्रिया अर्थात् verb की III form से पहले ‘not’ का प्रयोग करते हैं।
Examples
1. क्या मैं एक पत्र नहीं लिख चुका हूँ? — Have I not written a letter?
2. क्या मैंने एक पत्र नहीं लिखा है? — Have I not written a letter ?
3. क्या तुम जयपुर नहीं देख चुके हो? — Have you not seen Jaipur?
4. क्या वह भोजन नहीं पका चुकी है? — Has she not cooked food?
5. उसने क्या नहीं पकाया है? — What has she not cooked?
6. तुमने क्या नहीं खाया है? — What have you not eaten?
7. वे कहाँ नहीं गये हैं? — Where have they not gone?
8. तुमने एक कहानी क्यों नहीं लिखी है? — Why have you not written a story?
प्रयोग (Uses)
1. Present Perfect में हमारी रुचि वर्तमान में होती है। कार्य भूतकाल में कभी शुरू हुआ किन्तु वर्तमान क्षण तक समाप्त हो चुका है तथा उसका एक निश्चित परिणाम सामने आ चुका है। जैसे
I have polished my shoes. (परिणाम-अब जूते चमकदार दिखाई दे रहे हैं।)
I have already taken two cups of tea. (परिणाम अब मैं और अधिक चाय नहीं पीना चाहता।)
2. जब main clause (मुख्य उपवाक्य) future tense में हो तो adverb clause of time में इस tense का use करें।
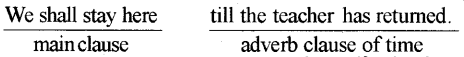
3. Repeated actions (बारंबारता वाले कार्यों) में भी इस tense का प्रयोग करें।
I have visited Ajmer lots of times.
4. State (स्थिति) बताने के लिए भी इस tense का प्रयोग किया जा सकता है।
I have always known about you.
For तथा Since का प्रयोग
इस Tense में समयावधि (Period of Time) तथा समय-बिन्दु (Point of Time) बताने के लिए क्रमशः for एवं since का प्रयोग किया जाता है। जैसे
I have played for three hours.
I have played since 8 in the morning. (अब 11 बजे हैं।).
यहाँ three hours समयावधि है तथा 8 बजे का समय समय-बिन्दु है जहाँ से गिनना है।
Golden Rules
1. गिना-गिनाया समय (समयावधि) दिये होने पर for का प्रयोग (three hours, three days अदि)
2. समय-बिन्दु दिया होने पर since का प्रयोग (since 15th August, since 1996, since 8 o’clock अदि।)
Exercise 3.
Put the verbs in brackets into the Present Perfect Tense.
1. How long have you known Mr. Malik ? – I (know) him for five years.
2. I (not drive) a car yet.
3. We (live) here since 1980.
4. I (not fly) in a helicopter yet.
5. I (not see) him for several weeks.
6. I (not do) rock-climbing yet.
7. They (not remove) the heap of rubbish yet.
8. Would you like some tea ? I (just, prepare) some.
9. I often see him but I never (speak) to him.
10. I. (not pay) the electricity bill yet.
Answers :
1. have known
2. have not driven
3. have lived
4. have not flown
5. have not seen
6. have not done
7. have not removed
8. have just prepared
9. have never spoken
10. have not paid
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
or
Present Perfect Progressive Tense
आशय-Present Perfect Continuous Tense में तीन प्रमुख तत्त्व होते हैं
प्रथम, कार्य Past Tense में प्रारम्भ हो गया हो, द्वितीय, वही कार्य वर्तमान समय में भी चल रहा हो, और
तृतीय, वही कार्य कदाचित् भविष्य में भी चलता रहेगा।
नोट-इस Tense में प्रायः Static verb (मन्थर गति वाले Verb) का प्रयोग होता है। Static verbs के कुछ उदाहरण ये हैं – live, study, learn, rest (आराम करना), lie (पड़ा होना), stay, sit, stand, wait…… आदि।
पहचान-
1. हिन्दी में ऐसे वाक्य के अन्त में रहा है, रही है, रहा हूँ, रहे हैं ……. आदि शब्द आते हैं।
2. ऐसे वाक्यों में समय अवश्य दिया होता है।
3. मुख्य पहचान यह है-समय के बाद ‘से’ अवश्य दिया होता है। यदि समय तो दिया हो किन्तु समय के साथ ‘से’ नहीं हो तो वह Perfect Continuous Tense नहीं है।
जैसे वह सुबह पढ़ रहा है। — (Present Continuous Tense)
वह सुबह से पढ़ रहा है। — (Present Perfect Continuous)
वह सुबह पढ़ रहा था। — (Past Continuous)
वह सुबह से पढ़ रहा था। — (Past Perfect Continuous)
Present Continuous तथा Present Perfect Continuous Tense में अन्तर-Present Continuous Tense में प्रायः समय नहीं दिया होता है। यदि समय दिया हो तो उसके साथ ‘से’ कभी नहीं आता है। Present Perfect Continuous Tense में ‘समय’ अवश्य दिया होता है और समय के साथ ‘से’ अवश्य लगा होता है।
Golden Rules : ऐसे वाक्यों के अंग्रेजी में अनुवाद के नियम निम्नलिखित हैं
1. सबसे पहले Subject लिखो।
2. Subject के बाद आवश्यकतानुसार has been या have been लगाओ। Singular Subject के साथ has been आयेगा, और शेष सभी के साथ have been आयेगा।
3. मुख्य verb में -ing जोड़ दो।
4. ‘समय’ से पहले नियमानुसार ‘for’ अथवा ‘since’ का प्रयोग करो। सूत्र (Formula)-S + has been/have been + verb में -ing + for/since+time
‘for’ का प्रयोग-for का प्रयोग ‘समय की अवधि’ (Period of Time) के लिए होता है। यदि वाक्य में -घण्टे, -दिन, -सप्ताह, -महीने, -वर्ष शब्द दिये हुए हों तो ‘for’ का प्रयोग होगा। —
जैसेतीन घण्टे से — for three hours — (घण्टे)
दो सप्ताह से — for two weeks — (सप्ताह)
सात महीने से — for seven months — (महीने)
दो वर्षों से — for two years — (वर्ष)
‘since’ का प्रयोग-since का प्रयोग ‘निश्चित समय’ (Point of Time) के लिए होता है। घड़ी का समय (बजे), दिन का नाम, दिन व तारीख, महीने का नाम, सन्……. आदि के साथ ‘since’ का प्रयोग होता है। जैसे
since 3 o’clock — (घड़ी का समय) — since night (since last night)
since Monday — (दिन का नाम) — since noon
since 10 March (दिन व तारीख) — since yesterday
since July — (महीने का नाम) — since last (week/month) लेकिन for the last (week/month)
since 1990 (सन्) — since birth — (जन्म से)
since morning — since (he came) — जबसे (वह आया है)
since evening — since (he went) — जबसे (वह गया है)
Examples
1. मैं सुबह से यह उपन्यास पढ़ रहा हूँ। — I have been reading this novel since morning.
2. तुम्हारा भाई यहाँ दो घण्टे से प्रतीक्षा कर रहा — Your brother has been waiting here for two hours.
3. विद्यार्थी मार्च से कठिन परिश्रम कर रहे हैं | — The students have been working hard since March.
4. वे सन् 1999 से जयपुर में रह रहे हैं। — They have been living in Jaipur since 1999.
5. हम पिछले सप्ताह से हमारे मकान की — We have been cleaning our house since last सफाई कर रहे हैं। week.
6. हरीश सोमवार से एक कहानी लिख रहा है। — Harish has been writing a story since Monday.
Negative-Present Perfect Continuous (Negative) में not हमेशा been के पहले आता है अर्थात् has/have के बाद आता है। दूसरे शब्दों में, not को has/have और been के बीच में रखो।
सूत्र (Formula) – S + has/have not been + verb में -ing…..
Interrogative – Present Perfect Continuous (Interrogative)
(a) Has/Have से वाक्य आरम्भ करो,
(b) इसके बाद Subject लाओ,
(c) been को verb में -ing के पहले रखो।
सूत्र (Formula)-Has/Have+Subject + been + verb में –ing……
Interrogative-Negative-Present Perfect Continuous (Interrogative-Negative) में
(a) Has/Have से वाक्य आरम्भ करो,
(b) इसके बाद Subject रखो।
(c) फिर not रखो,
(d) इसके बाद been रखो।
सूत्र (Formula)-Has/Have + S + not + been + verb में -ing…..
Examples – Negative
1. मैं सुबह से यह उपन्यास नहीं पढ़ रहा हूँ। — I have not been reading this novel since morning.
2. सीता शाम से भोजन नहीं पका रही है। — Sita has not been cooking food since evening
3. वह सन् 1999 से जयपुर में नहीं रह रहा है। — He has not been living in Jaipur since 1999.
4. वे दो घंटे से अपना पाठ याद नहीं कर रहे हैं। — They have not been learning their lesson for two hours.
5. हम पिछले सप्ताह से अपने कमरे की सफाई नहीं कर रहे हैं। — We have not been cleaning our room since last week.
6. तुम्हारा भाई पिछले छः महीने से इस दफ्तर में काम नहीं कर रहा है। — Your brother has not been working in this office for last six months.
7. वह तीन दिनों से मुझे नहीं पढ़ा रहा है। He has not been teaching me for three days.
Interrogative
1. क्या मैं सुबह से यह उपन्यास पढ़ रहा हूँ? — Have I been reading this novel since morning ?
2. क्या सीता शाम से भोजन पका रही है? — Has Sita been cooking food since evening?
3. क्या हम छ: वर्षों से जयपुर में रह रहे हैं? — Have we been living in Jaipur for six years?
Interrogative-Negative
1. क्या मैं सुबह से यह उपन्यास नहीं पढ़ रहा हूँ? — Have I not been reading this novel since morning?
2. क्या सीता रात से भोजन नहीं पका रही है? — Has Sita not been cooking food since night?
3. क्या हम मार्च से जयपुर में नहीं रह रहे हैं? — Have we not been living in Jaipur since March?
4. क्या वह शुक्रवार से मुझे नहीं पढ़ा रहा है? — Has he not been teaching me since Friday?
प्रयोग (Uses) –
1. ऐसे कार्य के साथ जो भूतकाल में किसी समय आरंभ हुआ और अभी भी जारी
The students have been reading English for three months.
2. अब तक repeat किये जा रहे actions के साथ इस tense का use कर सकते हैं।
I have been going to morning classes of Mathematics.
3. ऐसे actions व situations जो just stopped (हाल ही में बंद) हुए हैं।
You look hot : Yes, I have been runnning.
Exercise 4.
Put the verbs in brackets into the Present Perfect Continuous Tense.
1. I (shop) all day and now I am completely exhausted.
2. It (drizzle) since morning.
3. They (attend) classes since last week.
4. The doctors (try) to revive the patient but they have not succeeded so far.
5. They (build) that bridge for over three years but have not completed it yet.
6. Her phone (ring) for ten minutes. I wonder why she doesn’t answer it.
7. Someone (use) my fountain pen. The nib is all bent.
8. It (rain) for three days now. There will be a flood soon.
9. We (argue) about this for two hours now. Don’t you think we should stop ?
10. Mary (weep) No, she (not weep), she (peel) onions.
Answers :
1. have been shopping
2. has been drizzling
3. have been attending
4. have been trying
5. have been building
6. has been ringing
7. has been using
8. has been raining
9. have been arguing
10. Has Mary been weeping, has not been weeping, has been peeling.
Past व Future के Sentence Structures जो Present Time को refer करते हैं।
1. Simple Past indicating Present Time.

2. Simple Future Indicating Present Time. will be about nineteen.
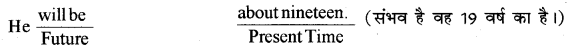
5. Past Indefinite Tense
or
Simple Past Tense
आशय-यह Tense भूतकाल की सूचना देता है। यह Tense कार्य की पूर्ण समाप्ति का सूचक है। इस Tense का प्रयोग तब किया जाता है जबकि कार्य के साथ-साथ समय भी समाप्त हो जाता है। जैसे, “वह कल दिल्ली गया।” इसमें ‘दिल्ली जाने का कार्य व ‘कल’ दोनों ही समाप्त हो चुके हैं, अतः यह Simple Past Tense है।
पहचान-
1. हिन्दी में ऐसे वाक्यों में verb (क्रिया) के अन्त में प्रायःT,, अथवा -या, -ये, -ई अथवा -या था, -ये थे, -ई थी आदि शब्द आते हैं।
2. कभी-कभी समय के निर्धारण के लिए इस Tense में Past Tense सूचक Adverb (जैसेon Sunday, on Monday, on Friday, in March, in June, in 1990, in 1985……. आदि शब्द) भी दे दिए जाते हैं।
Very Important (अतिमहत्त्वपूर्ण)
कभी-कभी विद्यार्थियों को Past Indefinite तथा Present Perfect Tense में Confusion (गलतफहमी) हो जाता है। इसे दूर करने के लिए निम्नलिखित पर ध्यान दो
मैंने एक पत्र लिखा। — I wrote a letter. (Past Ind.)
मैंने एक पत्र लिखा था। — I wrote a letter. (Past Ind.)
मैंने एक पत्र लिखा है। — I have written a letter. (Present. Perfect)
ध्यान दें
1. यदि verb (क्रिया) के अन्त में केवल -या, -ये, -ई आदि हों तो Past Indefinite Tense है। जैसे
मैंने उसे पढ़ाया। — I taught him.
वह शाम को फुटबाल खेला। — He played football in the evening.
2. यदि Verb (क्रिया) में -या, -ये, -ई आदि के बाद ‘था’ हो तो भी यह Past Indefinite Tense है। जैसे मैंने उसे पढ़ाया था। I taught him.
3. यदि verb (क्रिया) में -या, -ये, -ई आदि के बाद ‘है’ या ‘हैं’ हो तो यह Present Perfect Tense है। जैसेमैंने उसे पढ़ाया है।
I have taught him. इस अन्तर को ध्यान से समझो।
Golden Rules : ऐसे वाक्यों में हमेशा verb की II Form (past Tense) का ही प्रयोग होता है। Person, Number व Gender से कोई अंतर नहीं पड़ता है।।
सूत्र (Formula)-Sub. + V की II Form…..
Negative Sentences – Past Indefinite Tense वाले वाक्यों को Negative बनाने में प्रायः विद्यार्थी गलती करते हैं। अतः इसे ध्यान से मनन करें। ऐसे वाक्यों का Negative बनाने के लिए सदैव did not का प्रयोग किया जाता है, किन्तु Past Tense के verb को I Form में अर्थात् Present Tense में अवश्य ही बदलना होगा। विद्यार्थी did भी लगा देते हैं और verb की II form को नहीं बदलते हैं, जो कि एक भयंकर गलती है।
सूत्र (Formula)-S + did not + verb की I Form…..
Examples
1. मैं फुटबाल खेला। — I played football.
2: मैं फुटबाल नहीं खेला। — I did not play football.
3. तुम बाजार गये थे। — You went to market.
4. तुम बाजार नहीं गये थे। — You did not go to market.
5. विमला ने एक गाना गाया। — Vimla sang a song.
6. विमला ने एक गाना नहीं गाया। — Vimla did not sing a song.
7. मुकेश ने एक कहानी लिखी थी। — Mukesh wrote a story.
8. मुकेश ने एक कहानी नहीं लिखी। — Mukesh did not write a story.
9. अध्यापक ने मुझे कल पढ़ाया था। — The teacher taught me yesterday.
10. अध्यापक ने कल मुझे नहीं पढ़ाया था। — The teacher did not teach me yesterday.
Interrogative Sentences
Interrogative – Negative
Rule :
1. Past Indefinite Tense के Interrogative वाक्य सदैव Did से आरम्भ होंगे। Did के बाद Subject, फिर verb की I form आयेगी।
2. यदि Question word (अर्थात् Wh-) से प्रश्नवाचक बनाना हो तो सबसे पहले Wh- आयेगा उसके बाद did आयेगा। सूत्र (Formula)
(i) Did + S + verb की I form +………?
(ii) Wh- + did + S + verb की I form + ………?
3. Interrogative-Negative वाक्यों में not Subject के बाद किन्तु मुख्य verb के पहले आयेगा। सूत्र (Formula) – Did + S + not + verb की I form…..?
Examples :
1. क्या वह कल अजमेर गया?
Did he go to Ajmer yesterday?
2. क्या वह कल अजमेर नहीं गया था?
Did he not go to Ajmer yesterday?
3. क्या सीता ने चावल पकाए थे?
Did Sita cook rice?
4. क्या सीता ने चावल नहीं पकाए थे?
Did Sita not cook rice?
5. क्या अध्यापक ने तुम्हें सजा दी थी?
Did the teacher punish you?
6. क्या अध्यापक ने तुम्हें सजा नहीं दी थी?
Did the teacher not punish you?
7. क्या वह जयपुर में एक सप्ताह ठहरा?
Did he stay at Jaipur for a week?
8. क्या वह जयपुर में एक सप्ताह नहीं ठहरा था?
Did he not stay at Jaipur for a week?
9. वह जयपुर में कब ठहरा था?
When did he stay at Jaipur?
प्रयोग (Uses)
(1) With past actions when the time of an action is mentioned or implied.
ऐसे Past actions के साथ जिसमें कार्य का समय या तो बताया गया है या निहित है।
नोट : ago, yesterday, last, previous आदि adverbs का use हो सकता है।
1. बचपन में लेखक की देखभाल दादी ने की।
Granny looked after the author in childhood.
2. चिड़ियाओं ने रोटी के टुकड़े नहीं खाये।
The sparrows did not eat the crumbs of bread.
(2) In ‘improbable conditional sentences’.
असम्भाव्यता-शर्त वाले वाक्यों में।
1. यदि आप कठिन परिश्रम करते तो आप उत्तीर्ण हो जाते।
If you worked hard, you would pass.
2. काश मैं पक्षी होता तो मैं उड़ता।
Were I a bird I would fly.
Exercise : 5
Put the verbs in brackets into the Past Indefinite Tense :
1. Columbus (discover) America more than 400 years ago.
2. Jawaharlal Nehru always (go) to Manali in holidays.
3. When I was in Kerala, I daily (drink) coconut milk.
4. As soon as we left the house, it (begin) to drizzle.
5. He (lose) his way in the Jungle.
Answers :
1. discovered
2. went
3. drank
4. began
5. lost
6. Past Continuous Tense
or
Past Progressive Tense
आशय-जब कोई वाक्य यह प्रकट करता है कि कोई कार्य भूतकाल में (किसी दिए हुए समय पर) चल रहा था, तो यह Past Continuous अथवा Past Progressive Tense होता है।
पहचान-हिन्दी में ऐसे वाक्यों में क्रिया के तुरन्त बाद -रहा था, -रहे थे, -रही थी, शब्द आते हैं।
Golden Rules :
1. ऐसे वाक्यों में Subject सबसे पहले लाओ।
2. उसके बाद नियमानुसार was अथवा were का प्रयोग करो।
3. अब verb की I form में -ing जोड़ो।
सूत्र (Formula) – S + was/were + verb में – ing…..
Examples
1. तुम उस समय स्कूल जा रहे थे।
You were going to school at that time.
2. लीला सुबह गाना गा रही थी।
Leela was singing a song in the morning.
3. माता हमारा नाश्ता तैयार कर रही थी।
Mother was preparing our breakfast.
4. पिताजी सुबह नहा रहे थे।
Father was taking a bath in the morning.
5. माताजी दोपहर में सो रही थीं।
Mother was sleeping in the afternoon.
Past Continuous – Negative :
पहचान – ऐसे वाक्यों में Verb (क्रिया) के पहले ‘नहीं’ शब्द होता है। जैसे – तुम कल स्कूल नहीं जा रहे थे।
Golden Rule :
Rule : 1. ऐसे वाक्यों में Subject सबसे पहले लाओ।
Rule : 2. इसके बाद नियमानुसार was अथवा were का प्रयोग करो।
Rule : 3. इसके बाद ‘not’ लगाओ। ध्यान दे, ‘not’ सदैव तीसरे स्थान पर आता है।
Rule : 4. अब verb की I Form में -ing जोड़ो। सूत्र (Formula) – S + was/were + not + verb में -ing…..
Examples
1. तुम तब स्कूल नहीं जा रहे थे।
You were not going to school them.
2. लीला सुबह गाना नहीं गा रही थी।
Leela was not singing a song in the morning.
3. माता हमारा नाश्ता तैयार नहीं कर रही थी।
Mother was not preparing our breakfast.
4. पिताजी सुबह नहीं नहा रहे थे।
Father was not bathing in the morning.
5. माताजी दोपहर में नहीं सो रही थीं।
Mother was not sleeping in the afternoon.
Past Continuous-Interrogative :
पहचान – ऐसे वाक्यों के आरम्भ में ‘क्या’ शब्द आता है।
क्या तुम कल स्कूल जा रहे थे?
Golden Rule :
Rule : 1. आवश्यकतानुसार सबसे पहले was अथवा were लगाओ।
Rule : 2. इसके बाद Subject लगाओ।
Rule : 3. इसके बाद Verb की I Form में -ing लगाओ।
Rule : 4. अन्त में प्रश्नवाचक चिह्न (?) लगाओ।
Examples
1. क्या तुम स्कूल जा रहे थे?
Were you going to school?
2. क्या लीला सुबह गाना गा रही थी?
Was Leela singing a song in the morning?
3. क्या माता हमारा नाश्ता तैयार कर रही थी?
Was mother preparing our breakfast?
4. क्या पिताजी सुबह नहा रहे थे?
Was father taking a bath in the morning?
5. क्या माताजी दोपहर में सो रही थीं?
Was mother sleeping in the afternoon?
Past Continuous-Interrogative-negative
पहचान-
(1) ऐसे वाक्य ‘क्या’ से आरम्भ होते हैं।
(2) Verb (क्रिया) के पहले ‘नहीं’ शब्द होता है। जैसे- क्या तुम स्कूल नहीं जा रहे थे।
Golden Rules :
Rule : 1. आवश्यकतानुसार सबसे पहले was अथवा were लगाओ।
Rule : 2. इसके बाद Subject लगाओ।
Rule : 3. इसके बाद ‘not’ लगाओ। ध्यान दें : ‘not’ सदैव तीसरे स्थान पर आता है।
Rule : 4. इसके बाद Verb की I Form में -ing लगाओ।
Rule : 5. वाक्य के अन्त में प्रश्नवाचक चिह्न (?) लगाओ।
Examples
1. क्या तुम स्कूल नहीं जा रहे थे?
Were you not going to school?
2. क्या लीला सुबह गाना नहीं गा रही थी?
Was Leela not singing a song in the morning?
3. क्या माता हमारा नाश्ता तैयार नहीं कर रही थी?
Was Mother not preparing our breakfast?
4. क्या पिताजी सुबह नहीं नहा रहे थे?
Was father not taking bath in the morming?
5. क्या माताजी दोपहर में नहीं सो रही थीं?
Was Mother not sleeping in the afternoon?
Exercise 6.
Put the verbs in brackets into the Past Continuous Tense :
1. The children were frightened because it (get) dark.
2. It was a fine day and the roads were crowded because a lot of people (rush) to the sea-side.
3. Two children (play) on the sand and two fishermen (lean) against an upturned boat.
4. My wife and I (talk) about you the other day.
5. Geeta said that she (try) to lose weight.
Answers :
1. was getting
2. were rushing
3. were playing, were leaning
4. were talking
5. was trying.
7. Past Perfect Tense
आशय-Past Perfect Tense के प्रमुख लक्षण निम्नलिखित हैं
1. भूतकाल में दो कार्य हुए हों,
2. दोनों ही कार्य पूरे हो गये हों,
3. ऐसी दशा में दोनों ही कार्य एक-साथ समाप्त नहीं हो सकते हैं। एक कार्य पहले समाप्त होता है, और दूसरा कार्य बाद में समाप्त होता है। पहले समाप्त हुआ कार्य वाला वाक्य Past Perfect Tense का होता है।
नोट-इस Tense के वाक्य प्राय: Complex होते हैं।
पहचान-हिन्दी में ऐसे वाक्यों में मुख्य क्रिया के बाद -चुका था, -चुकी थी, -चुके थे, अथवा -लिया था, -लिए थे, या -ली थी शब्द आते हैं, और वाक्य भी प्रायः वहीं समाप्त हो जाता है। जैसे – मेरे स्टेशन पहुँचने से पहले गाड़ी रवाना हो चुकी थी।
Rules :
1. जो कार्य पहले समाप्त हो चुका है, उसमें had + verb की III form लाओ।
2. जो कार्य बाद में समाप्त हुआ है, उसमें verb की II form लाओ। जैसेमेरे स्टेशन पहुंचने से पहले गाड़ी रवाना हो चुकी थी। The train had departed before I reached the station.
3. ऐसे वाक्यों के बीच में प्रायः before या after का प्रयोग होता है।
इस Sentence में दो कार्य भूतकाल में हुए हैं – प्रथम, मेरा स्टेशन पर पहुँचना, और द्वितीय गाड़ी का जाना। अब ध्यान से देखने पर ज्ञात होता है कि गाड़ी के जाने का काम पहले हुआ इसलिए इस वाक्य में had + verb की III form का प्रयोग किया (The train had gone), दूसरी क्रिया अर्थात् मेरे स्टेशन पर पहुँचने का कार्य बाद में हुआ, अतः इसके साथ verb की II form प्रयोग की गई है – (I reached the station).
Golden Rule : ऐसे वाक्यों में यह देखने के लिए कि कौनसा काम (क्रिया) पहले हुआ है और कौनसा बाद में उलझन हो सकती है। अतः इसके लिए Golden Rule यह है
1. वाक्य के जिस भाग में ‘चुका था’ शब्द है, उस वाक्य का अनुवाद पहले करो और उसके साथ ही had आयेगा। had के बाद verb की III form आती है।
2. शेष दूसरे वाक्य में verb की II form आती है।
एक Golden Rule इसे भी समझिए —
1. ‘before’ का अर्थ है – ‘पहले’ तो ‘before’ के पहले वाले वाक्य में had + Verb की III form आयेगी, तो दूसरे वाक्य में verb की II form आयेगी।
2. ‘after’ का अर्थ है – ‘बाद में’ तो after के बाद वाले वाक्य में had + verb की III form आयेगी, तो after के पहले वाले वाक्य में verb की II form आयेगी। जैसे
1. डॉक्टर के आने से पहले मरीज मर चुका था। .
The patient had died before the doctor came.
(before के पहले had का प्रयोग किया है।) –
2. मेरे स्कूल जाने के बाद माता ने मेरी कमीज धोई।
My mother washed my shirt after I had gone to school.
(after का’ अर्थ है ‘बाद में’ तो after के बाद had का प्रयोग किया है।)
Negative Sentence में had के तुरन्त बाद ‘not’ आयेगा।
Interrogative Sentences – Had से आरम्भ होते हैं।
Interrogative-Negative Sentence में – Had से वाक्य आरम्भ होगा तथा not verb की III form के पहले आयेगा।
Examples
1. मेरे स्टेशन पहुंचने से पहले गाड़ी जा चुकी थी। — The train had departed before I reached the station.
2. डॉक्टर के आने के पहले रोगी मर चुका था। The patient had died before the doctor came.
3. पिताजी के आने के पहले माता भोजन पका चुकी थी। — Mother had cooked food before father came.
4. घण्टी बजने से पहले मैं स्कूल पहुँच गया था। — I had reached school before the bell rang.
5. जब मैं उसके घर पहँचा तो वह भोजन नहीं | — When I reached his house he had not taken his food.
6. क्या गाड़ी आने से पहले तुम स्टेशन नहीं पहुँच चुके थे? — Had you not reached the station before the train reached at the station ?
Exercise 7.
Put the verbs given in brackets into the Past Perfect Tense
1. When she ran out of petrol, she (cover) a long distance.
2. He (die) when the ambulance arrived.
3. I (never, be) abroad before I visited Sri Lanka.
4. We were sorry to find that the villagers (cut) down many beautiful trees for firewood.
5. In my childhood we used to play in a vast ground outside our city. Now when I went there I found that the construction of buildings (swallow up) the whole ground.
6. He refused to admit that he (make) a mistake.
7. He (not speak) a word of German before he married a German girl.
8. As soon as they (collect) enough money, they started building the hospital.
9. After the workers (finish) their day’s work, they went home.
10. I did not know the man because I (not see) him before.
Answers :
1. had covered
2. had died
3. had never been
4. had cut
5. had swallowed up
6. had made
7. had not spoken
8. had collected
9. had finished
10. had not seen
8. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
आशय-यह Tense, भूतकाल में हुए उन कार्यों व घटनाओं का वर्णन करने के लिए होता है, जो भूतकाल में एक निश्चित समय अवधि तक जारी रहें।
पहचान :
1. समय के साथ ‘से’ शब्द अवश्य होता है।
2. इसके पश्चात् रहा था, रहे थे, रही थी-शब्द आते हैं।
Rule : 1 : प्रत्येक Subject के साथ had been का प्रयोग होता है।
Rule : 2 : Verb की First Form के साथ -ing जोड़ते हैं ।
Rule : 3 : निश्चित समय बिन्दु (Point of Time) के लिए since तथा समय की अवधि (Period of Time) के लिए for का प्रयोग करते हैं।
सूत्र (Formula)-Sub. + had been + verb में ing + Object…..sincelfor….
Example : सीता सुबह से भोजन पका रही थी।
Sita had been cooking food since morning. प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों में
Rules : ‘had’ को कर्ता (Subject) के पहले रखते हैं।
‘been’ को मुख्य verb के पहले रखते हैं। वाक्य के अन्त में प्रश्नवाचक चिह्न लगाओ। शेष नियम यथावत् हैं।
Example- क्या सीता सुबह से भोजन पका रही थी?
Had Sita been cooking food since morning?
सूत्र (Formula)-Had + Sub. + been + V में -ing + object ….sincelfor……..? नकारात्मक वाक्यों में
Rule : वाक्य में had और been के बीच में not का प्रयोग करो। शेष नियम यथावत् हैं
Example : सीता सुबह से भोजन नहीं पका रही थी।
Sita had not been cooking food since morning.
सूत्र (Formula)
Sub + had + not + been + V में -ing + object…..sincel for……. प्रश्नवाचक-नकारात्मक वाक्यों में
Rule :
1. Had से वाक्य आरम्भ करो। .
2. Subject लाओ।
3. not लाओ।
4. not के तुरन्त बाद been लाओ।
5. Verb की I Form में -ing लगाओ।
6. वाक्य के अन्त में प्रश्नवाचक चिह्न लगाओ।
Example : क्या सीता सुबह से भोजन नहीं पका रही थी?
Had Sita not been cooking food since morning? सूत्र (Formula)
Had + Sub. + not + been + V में -ing + Obj. …..since/for…..
Examples Affirmative :
1. वह दो महीने से कहानियाँ लिख रहा था। — He had been writing stories for two months.
2. अध्यापक सोमवार से अंग्रेजी पढ़ा रहा था। — The teacher had been teaching English since Monday. Interrogative :
3. क्या तुम्हारा भाई दो घण्टे से फुटबाल खेल रहा था? — Had your brother been playing football for two hours?
4. क्या तुम सन् 2001 से जयपुर में रह रहे थे? थी? — Had you been living in Jaipur since 2001?
5. विमला तीन घण्टे से इस पुस्तक को नहीं पढ़| रही थी। — Vimla had not been reading this book for three hours.
6. कमला मार्च से इस काम को नहीं कर रही थी। — Kamla had not been doing this work since March. Interrogative-Negative :
7. क्या लड़के एक घण्टे से शोर नहीं कर रहे थे? — Had the boys not been making a noise for one hour?
8. क्या तुम्हारी माता सुबह से कपड़े नहीं धो रही — Had your mother not been washing clothes since morning?
Exercise 8.
Put the verbs in brackets into the Past Perfect Progressive Tense.
1. Einstein ……………(study) for one year when Mileva joind the university.
2. India …………. (struggle) for freedom since 1857.
3. She …………(extend) all the possible help for all the time she stayed with us.
4. Volcano ……….. (erupt) for three days when the succour reached there.
5. Citizens ………….(protect) trees since childhood.
Answers :
1. had been studying
2. had been struggling
3. had been extending
4. had been erupting
5. had been protecting.
9. Future Indefinite Tense
or
Simple Future Tense
आशय-जब कोई कार्य भविष्य में किया जायेगा तो इसका प्रयोग करते हैं।
पहचान-हिन्दी में ऐसे बाक्यों में verb (क्रिया) के बाद प्रायः -गा, -गी, -गे होते हैं।
Rules.:
1. ऐसे वाक्यों में shall अथवा will का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
2. shall तथा will के बाद verb की I form प्रयोग की जाती है। विशेष नोट-I तथा We के साथ shall का प्रयोग करो तथा शेष सभी (you, he, she, it, they, Ram, boy, boys….आदि) के साथ will का प्रयोग करो।
S + will/shall + V1……… Negative Sentences में shall/will के बाद not का प्रयोग करो।
– S + shall/will + not + V1………………
Interrogative Sentences में Shall या Will से वाक्य आरम्भ, उसके बाद Subject और verb की I form का प्रयोग करो।
Shall/will + S + V1………….. ?
Examples:
Affirmative :
1. मैं कल बाजार जाऊँगा। — I shall go to market tomorrow.
2. मेरी माता भोजन पकायेगी। — My mother will cook food.
3. विद्यार्थी फुटबाल खेलेंगे। — Students will play football.
4. हम रात को सोयेंगे। — We shall sleep at night.
Negative
5. तुम खाना नहीं खाओगे। — You will not take food.
6. मैं तुम्हें अपनी पुस्तक नहीं दूंगा। — I shall not give you my book.
7. सीता चाय तैयार नहीं करेगी। — Sita will not prepare tea.
8. हम आज सिनेमा नहीं जायेंगे। — We shall not go to cinema today
Interrogative
9. क्या अध्यापक आज पढ़ायेगा? — Will the teacher teach today?
10. क्या आज मैं जयपुर जाऊँगा? — Shall I go to Jaipur today?
11. क्या वह आज यह काम करेगा? — Will he do this work today?
12. क्या हम आज आम खाएंगे? — Shall we eat mangoes today?
Interrogative-Negative
13. क्या अध्यापक आज नहीं पढ़ायेगा? — Will the teacher not teach today?
14. क्या आज मैं जयपुर नहीं जाऊँगा? — Shall I not go to Jaipur today?
15. क्या वह आज यह काम नहीं करेगा? — Will he not do this work today?
प्रयोग (Uses)
(i) To express ‘pure future’ भविष्य के कार्य की सूचना के लिए
1. हम पढ़ाई करेंगे।
We shall study.
(ii) Shall I या Shall we का use किसी की wish (इच्छा), या instructions (निर्देश) जानने के लिए करें।
1. क्या मैं खिड़की बन्द कर लूँ?
Shall I close the window? (इच्छा जानना)
2. क्या हम घर के लिए रवाना हो जाएं?
Shall we leave for home? (निर्देश प्राप्त करना)
(iii) In conditional sentences expressing open/probable condition.
(शर्त वाले वाक्य जो भावी सम्भावना प्रकट करते हैं।)
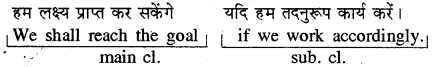
नोट : Simple Future का use, main clause में करें व Simple Present का use, sub. clause में करें।
Exercise 9.
Put the verbs in brackets into the Simple Future Tense :
1. …………. you ……….. (give) her my message on your way to home ?
2. I ………… (not have) to cook. I am joining a mess tomorrow.
3. I …………. (wait) here until she returns.
4. If you search your heart, you………..(find) me.
5. Do you think she ………… (recognise) me ?
6. You …………(feel) better when you have taken medicines.
7. Unless she runs, she ………….(not catch) the bus.
Answers :
1. Will, give
2. shall not have
3. shall wait
4. will find
5. will recognise
6. will feel
7. will not catch.
10. Future Continuous Tense
पहचान-ऐसे वाक्यों में हिन्दी में क्रिया के अन्त में -रहा होगा, -रहे होंगे, -रही होऊँगी आदि शब्द आते हैं।
Rule : Subject के बाद shall be/will be और उसके बाद verb की I form में -ing लगता है।
सूत्र (Formula)-S + shall be/will be + V में -ing…….
Negative : S + shall not be/will not be + V में – ing..
Interrogative : Shall/Will + S + be + V में – ing……?
Interrogative-Negative : Shall/Will + S + not be + V में -ing…..?
Examples .
1. मैं उसकी सहायता करता रहूँगा।
I shall be helping him.
2. बबीता भोजन पका रही होगी।
Babita will be cooking food.
3. विद्यार्थी मैच खेल रहे होंगे।
The students will be playing the match.
4. हम गाने गा रहे होंगे।
We will be singing songs.
5. तुम रात को सो रहे होंगे।
You will be sleeping at night.
6. क्या सीता नाच रही होगी?
Will Sita be dancing?
7. क्या वह अपना पाठ याद कर रहा होगा?
Will he be learning his lesson?
8. क्या अध्यापक नहीं पढ़ा रहा होगा?
Will the teacher not be teaching?
9. क्या सीता नहीं रो रही होगी? ।
Will Sita not be weeping?
10. क्या हम शोर नहीं कर रहे होंगे?
Shall we not be making a noise?
Exercise 10.
Put the verbs in brackets into the Future Continuous Tense.
1. When you next see me, I (wear) my new suit.
2. In a few days, time, we (fly) over the Himalayas.
3. In a hundred years, time, people (go) to the Mars for their holidays.
4. Air hostess : We (take off) in a minute. Please fasten your safety belts.
5. We are making a house-to-house collection for the earthquake victims. We (come) to your house also in day or so.
6. In a few years’ time we all (live) in air-conditioned houses.
7. It is beginning to get dark; the street lights (go on) in a few minutes.
Answers :
1. shall be wearing
2. shall be flying
3. will be going
4 shall be taking off
5. shall be coming
6. shall be living
7. will be going on.
11. Future Perfect Tense
प्रयोग – इस tense का प्रयोग उस समय किया जाता है जब किसी निश्चित समय तक किसी कार्य के भविष्य काल में समाप्त होने की सम्भावना हो। यहाँ यह कल्पना की जाती है कि भविष्य में दिए गये समय तक कार्य पूरा हो चुकेगा।

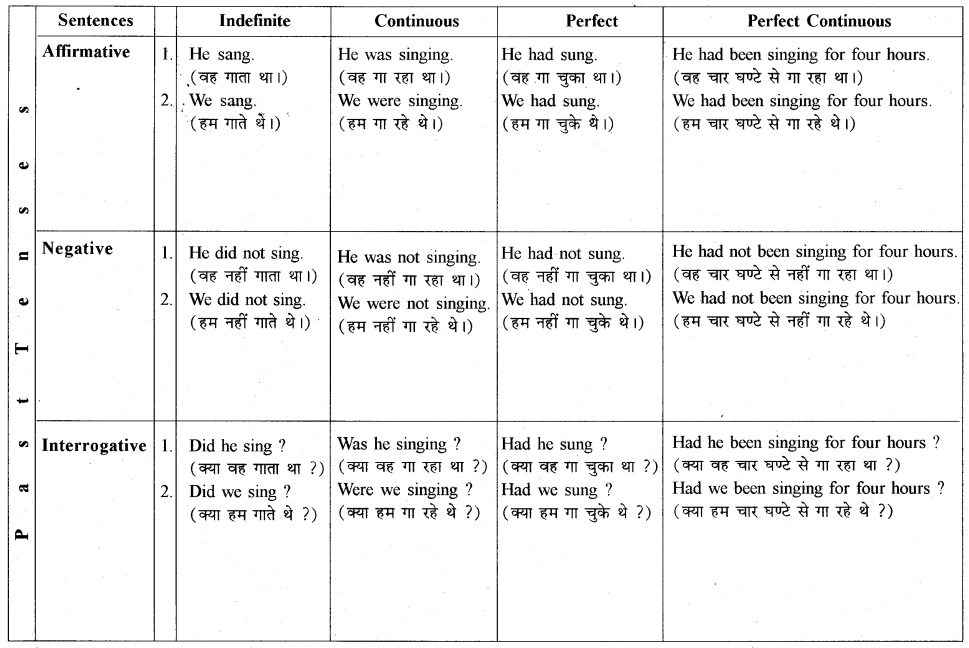
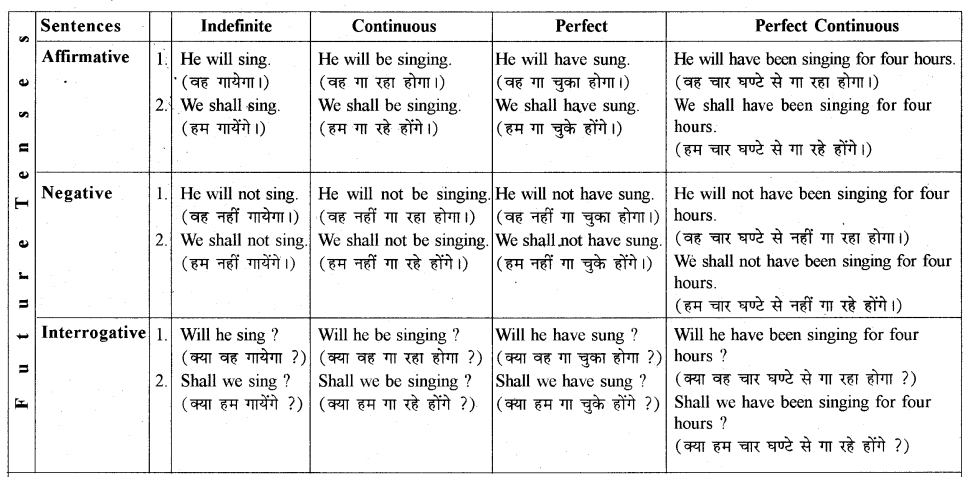
Note : इस Tense Chart को काम में लेते समय निम्न बातों पर ध्यान दें
1. सभी प्रथम वाक्य (No. 1 वाक्य) Singular Subject से सम्बन्धित हैं तथा सभी द्वितीय वाक्य (No. 2 वाक्य) Plural Subject से सम्बन्धित हैं।
2. यहाँ ‘sing’ क्रिया (verb) काम में ली गई है, जिसकी तीनों Forms इस प्रकार हैं – I Form sing II Form sang III Form sung.
3. I’ तथा ‘You’ subject को Plural Subject की तरह व्यवहार में लिया जाता है।
4. ‘I’ के साथ continuous में Present होने पर ‘am’ तथा Past होने पर ‘was’ helping verb लगता है।
5. Future Tense में ‘I’ और ‘We’ के साथ प्रायः shall तथा अन्य subjects के साथ will लगता है।
6. इस Chart के तुलनात्मक अध्ययन से आप Tense का ज्ञान आसानी से प्राप्त कर सकते हैं।
7. यहाँ वाक्यों के हिन्दी अर्थ भी साथ दिये गये हैं जिससे आपको Tense पहचानने में तथा समझने में बहुत सुविधा मिलेगी।
Golden Rules
for
Filling in Correct
Form of Verbs Present Indefinite Tense
Or
Simple Present tense
Rule 1: Modals (need not, must, can, could, shall, should, will, would, may, might, let)
के बाद हमेशा Verb की I Form ही आयेगी। जैसे
1. You must ……….. (cook) food for the guests.
Answer: You must cook food for the guests.
2. She can …………. (take) tea now.
Answer: She can take tea now.
3. I will …………… (give) you a watch.
Answer: I will give you a watch.
4. Sita should ……. (keep) a dog.
Answer:
Sita should keep a dog.
Rule 2 : always, every (day, month, week, year), usually, seldom, आदि प्रायः Present
Tense के सूचक हैं। अतःverb की I Form का प्रयोग होगा। जैसे
1. You always …………. (go) to school on foot.
Answer: You always go to school on foot.
2. He ………… (go) to cinema every Sunday.
Answer: He goes to cinema every Sunday
3. She seldom ………… (cook) food.
Answer: She seldom cooks food.
4. My brothers usually …………….. (go) to school together.
Answer: My brothers usually go to school together.
5. My uncle seldom ………… (carry) an umbrella.
Answer: My uncle seldom carries an umbrella.
Rule 3 : यदि वाक्य में सार्वभौम सत्य (universal truth), वैज्ञानिक तथ्य, आध्यात्मिक सत्य, मुहावरे,
कहावतें आदि हों तो Simple Present Tense का प्रयोग होता है। जैसे
1. The sun ………. (rise) in the east.
Answer: The sun rises in the east..
2. Fortune ……… (favour) the brave.
Answer: Fortune favours the brave.
Rule 4: निश्चित (fixed), स्थायी (permanent) अथवा सारणीबद्ध कार्यक्रमों (Tabled Programmes)
के लिए भी Simple Present Tense का प्रयोग होता है। जैसे
1. Our school ………….. (run) from 7.30 to 12.30.
Answer: Out school runs from 7.30 to 12.30.
2. The train ………….. (leave) for Agra at 6.05 a.m.
Answer: The train leaves for Agra at 6.05 a.m.
Past Indefinite Tense
Or
Simple Past Tense
Rule : 5: yesterday, last (week, month, year ……….), the other day आदि शब्द Past Tense
के सूचक हैं। यदि वाक्य में ये शब्द हों तो Verb की II Form आयेगी। जैसे–
1. He …………. (come) to see me last week.
Answer: He came to see me last week.
2. Yesterday I ………… (have) my shoes polished by a cobbler. (Causative Verb)
Answer: Yesterday I had my shoes polished by a cobbler.
3. His wife …………. (die) last year.
Answer: His wife died last year.
4. He ……….. (go) to Jaipur yesterday.
Answer: He went to Jaipur yesterday.
Rule : 6 : यदि वाक्य Past Tense में चालू हो तो प्रायः पूरा वाक्य Past Tense में चलेगा। जैसे
1. When I was cleaning my room, I ……. (hear) a loud noise.
Answer:
When I was cleaning my room, I heard a loud noise
2. Sita …………. (cook) food and went to market.
Answer: Sita cooked food and went to market.
Future Indefinite Tense
Or
Simple Future Tense
Rule : 7 : tomorrow, next (week, month, year) आदि Future Tense के सूचक हैं अतः verb के
पहले (I तथा We के साथ) shall तथा (शेष सभी के साथ) will आयेगा। जैसे
1. We ………. (meet) the teacher next week.
Answer: We shall meet the teacher next week.
2. He ………….. (go) to Jaipur tomorrow.
Answer: He will go to Jaipur tomorrow.
3. I …………. (return) in the next week.
Answer: I shall return in the next week.
4. Tomorrow I ………….. (give) you some money.
Answer: Tomorrow I shall give you some money.
Perfect Tense
Rule : 8 : यदि वाक्य में just, yet अथवा up to now हो तो इन शब्दों के साथ has/ have+verb की III
Form आयेगी, had नहीं आयेगा। यदि वाक्य में already हो तो आवश्यकतानुसार has/have/had + verb की III Form …… कोई भी आ सकता है। जैसे
1. The doctor is not at home. He ……..(go) to hospital just now.
Answer: The doctor is not at home. He has gone to hospital just now.
2. He …………….. (already finish) his work and went to the cinema.
Answer: He had already finished his work and went to the cinema.
3. He …… (already finish) his work and now he will go to the cinema.
Answer: He has already finished his work and now he will go to the cinema.
Past Perfect Tense
[वाक्य के बीच में ‘before’ होने पर]
Rule: 9 (a): | यदि वाक्य में ‘before’ के पहले had (+ verb की III Form) हो तो before के बाद
verb की II Form आयेगी। जैसे
1. The guest had gone before I …………. (reach) the house.
Answer: The guest had gone before I reached the house.
2. The patient had died before the doctor….. (come)
Answer: The patient had died before the doctor came.
Rule : 9(b) : यदि वाक्य में before के बाद verb की II Form हो तो before के पहले वाक्यांश में had + verb की III Form आयेगी। जैसे
1. Mother …………… (cook) food before father came.
Answer: Mother had cooked food before father came.
2. We …………. (eat) mangoes before they went.
Answer: We had eaten mangoes before they went.
Note : Passive voice में had been + V की III Form आयेगी की|
1. The water tank ………… (clean) before it was filled.
Answer: The water tank had been cleaned before it was filled.
2. The truck ……. (load) by them before I reached there.
Answer: The truck had been loaded by them before I reached there.
Rule 10 (a) : यदि वाक्य में before के पहले Verb की I Form हो तो before के बाद भी Verb की
Form आयेगी। दूसरे शब्दों में, यदि before के एक ओर Present Tense हो तो before के दूसरी ओर भी Present Tense होगा। जैसे
1. He ………….. (take) milk before he goes to bed.
Answer: He takes milk before he goes to bed.
2. My mother prepares tea before father ……………… (come) from the office…
Answer: My mother prepares tea before father comes from the office.
[वाक्य के बीच में ‘after’ होने पर ]
Rule : 10(b): यदि वाक्य में after के पहले Verb की II Form (Past Tense) हो तो after के बाद had + Verb की III Form आयेगी। जैसे
1. My mother washed my shirt after I ………… (go) to school.
Answer: My mother washed my shirt after I had gone to school.
2. After I ……. (finish) my homework, I went to play.
Answer: After I had finished my homework, I went to play.
Rule : 10(c): यदि वाक्य में after के बाद had हो तो after के पहले Verb की II Form आयेगी। जैसे
1. He ……………. (go) to market after he had finished his work.
Answer: He went to market after he had finished his work.
Perfect Continuous Tense
Rule : 11 (a): यदि समय से पहले for, since अथवा all हो और वाक्य समाप्त हो गया हो तो
आवश्यकतानुसार has been अथवा have been + verb में -ing आयेगा (had been नहीं आयेगा).
1. Vimla ……….. (sleep) for two hours.
Answer: Vimla has been sleeping for two hours.
2. Raju …………. (read) since 4 o’clock.
Answer: Raju has been reading since 4 o’clock.
3. We …………. (live) in this house since 2010.
Answer: We have been living in this house since 2010.
4. The teacher ………….. (teach) for two months.
Answer:The teacher has been teaching for two months.
5. Sita …………. (cook) food since morning.
Answer: Sita has been cooking food since morning.
Rule : 11 (b) : यदि दो वाक्य दिए हुए हों और किसी भी एक वाक्य में समय से पहले for, since अथवा all दिया हो, और दूसरे वाक्य में Present Tense हो तो for, since, all के पहले has been, have
been + verb में – ing आयेगा।
1. She ………… (cook) rice for one hour and now she is reading
Answer : She has been cooking rice for one hour and now she is reading
2. He …………….. (wash) clothes since morning and he is tired.
Answer: He has been washing clothes since morning and he is tired.
3. Babita …………. (clean) the room for two days and she has not finished it yet.
Answer: Babita has been cleaning the room for two days and she has not cleaning it yet.
4. My father …………. (live) in Bikaner since 2015 but he has not left the house yet.
Answer: My father has been living in Bikaner since 2015 but he has not left the house yet.
5. You ……………. (work) hard since July and now you take rest.
Answer: You have been working hard since July and now you take rest.
Rule 11 (c): यदि दो वाक्य दिए हुए हों और किसी भी एक वाक्य में समय से पहले for, since अथवा all हो, और दूसरे वाक्य में verb की II Form अर्थात् Past Tense हो तो for, since अथवा all के पहले had been + verb में –ing आयेगा।
1. She …………….. (cook) food for one hour when she went to market.
Answer: She had been cooking food for one hour when she went to market.
2. The teacher ………….. (teach) for four hours when the students went to sleep.
Answer: The teacher had been teaching for four hours when the students went to sleep.
3. I ……….. (wash) clothes since morning when she came there.
Answer: I had been washing clothes since morning when she came there.
4. He ………….. (wait) for the train for two hours when it came.
Answer: He had been waiting for the train for two hours when it came.
5. It ……… (rain) all night and the roads were flooded.
Answer: It had been raining all night and the roads were flooded.
Rule : 11 (d) : यदि समय से पहले for, since अथवा all हो, और आगे वाक्य चालू हो, और इस आगे
वाक्य में yet या just हो तो (a) yet (या just) के कारण has (अथवा have) आयेगा, (b) for अथवा since के पहले has been (have been) + Verb में —ing आयेगा।
(a) yet (या just) के कारण has (अथवा have) आयेगा,
(b) for अथवा since के पहले has been (have been) + Verb में —ing आयेगा।
1. She ………… (write) a story for three hours but she (not finish) yet.
Answer: She has been writing a story for three hours but she has not finished yet.
2. I (do) homework all morning and I (not finish) it yet.
Answer: I have been doing homework all morning and I have not finished it yet.
नोट : यहाँ yet के कारण have आया है।
Future Perfect
Rule : 12 : यदि समय से पहले by हो तो-will have और verb की III Form (‘have’ के कारण) आयेगी। by’ के साथ प्रायः घड़ी का समय (जैसे-7 o’clock), दिनों का नाम (जैसे Sunday), महीनों का नाम (जैसे March), सन् (जैसे 2004), अथवा by this time-होता है। जैसे
1. She …………. (reach) Jaipur by this time.
Answer: She will have reached Jaipur by this time.
2. Babita …………….. (take) tea by 8 a.m.
Answer: Babita will have taken tea by 8 a.m.
3. By the end of this month he ……….. (finish) his course.
Answer: By the end of this month he will have finished his course.
4. The train ………. (leave) the station by the time we reach there.
Answer: The train will have left the station by the time we reach there.
5. By the end of this week, Uma …….. (spend) all the money.
Answer: By the end of this week, Uma will have spent all the money.
6. She …………….. (return) from England by 2025.
Answer:She will have returned from England by 2025.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
यह Tense बतलाता है कि भविष्य के जिस समय बिन्दु की हम कल्पना करते हैं, उस समय से पूर्व, वह कार्य प्रारम्भ हो चुका होगा, तथा भविष्य के उस समय तक कार्य चालू रहेगा तथा उसे चलते हुए कुछ समय हो चुका होगा।
ध्यातव्य बिन्दु
1. प्रश्न में प्रायः Future Tense सूचक शब्द [जैसे tomorrow, next (week, month, year …..), घड़ी का समय (8o’clock) …. आदि] के पहले प्रायः by शब्द होता है।
2. समय से पहले for, since अथवा all अवश्य होता है। अथवा |
3. वाक्य में when के बाद verb की I Form हो।
Rule 13. (A)Future Tense सूचक शब्द के कारण आवश्यकतानुसार shall अथवा will का प्रयोग करो।
(B) समय से पहले for, since अथवा all के कारण have been + verb में – ing लगाओ। जैसे
1. By the end of this year he ……………… (study) English for two years.
Answer: By the end of this year he will have been studying English for two years.
2. When I reach there, Sita ………… (wait) at the station for two hours.
Answer: When I reach there, Sita will have been waiting at the station for two hours.
3. When Sarla arrives here next month, you ………. (live) in this house for five years.
Answer: When Sarla arrives here next month, you will have been living in this house for five years.
4. They ………….. (play) for three hours by 7 o’clock this evening.
Answer: They will have been playing for three hours by 7 o’clock this evening.
Hints :
(1) समय से पहले for three hours है, इसलिए have been playing किया।
(2) समय से पहले by (7o’clock) है, इसलिए will लगाया।
5. The girls …………. (work) in this theatre for four years by the end of next month.
Answer: The girls will have been working in this theatre for four years by the end of nextmonth.
नोट : कभी (समय से पहले) by के स्थान पर ‘on’ भी आ सकता है। जैसे
6. Raju …….. (teach) English for twenty years on 10 March, 2023.
Answer: Raju will have been teaching English for twenty years on 10 March, 2023.
Imperative Sentences पहचान :Imperative वाक्य
(i) Verb की I Form से आरम्भ होते हैं, जैसे
(a) Listen ! Look ! ………..
(b) Bring, open, shut, write… अथवा
(ii) Do अथवा Do not से आरम्भ होते हैं, जैसेDo your work. Do not run on the road.
अथवा (iii) Please से आरम्भ होते हैं।
Rule 14 : Imperative वाक्य के बाद यदि दूसरा वाक्य भी चालू हो तो इस दूसरे वाक्य में हमेशा is
अथवा are अथवा am + verb में -ing आयेगा। was अथवा were कभी भी नहीं आयेंगे।
1. Look ! The man ……………. (run) after the bus, perhaps he ……… (want) to catch it.
Answer: Look ! The man is running after the bus, perhaps he wants to catch it. स्पष्टीकरण – पहला वाक्य (Look) imperative है, इसके बाद दूसरा वाक्य है इसलिए इस दूसरे वाक्य में is running किया। अब तीसरा वाक्य और चालू है। इसलिए इस तीसरे वाक्य में verb की I Form wants लगायी।
2. Don’t get out now, the train ……… (move) fast.
Answer: Don’t get out now, the train is moving fast.
3. Do not make a noise. Mother ……………. (sleep)
Answer: Do not make a noise. Mother is sleeping.
Rule : 15 : यदि Please से वाक्य चालू हो और उसके तुरन्त बाद ब्रैकिट में (not + verb की I Form)
हो तो Not के पहले हमेशा do और जोड़ दो। ध्यान रहे, does अथवा did गलत होगा। जैसे
1. Please ………………. (not make) a noise.
Answer: Please do not make a noise.
Miscellaneous Golden Rules
Rule 16. While, as (जबकि) शब्दों के बाद परिस्थिति के अनुसार
is, are, am]
was were ] + verb में -ing लगेगा। was, wered still (अभी तक) के बाद is, are, am तथा verb में -ing लगेगा, इसके बाद was अथवा were नहीं लगेगा। जैसे
1. He broke his leg while he ……….. (drive) a scooter.
Answer: He broke his leg while he was driving a scooter.
नोट : ‘broke’ से मालूम हुआ कि Past Tense है, इसलिए ‘was driving’ आयेगा।]
2. I saw a tall man while I ………….. (play) football.
Answer: I saw a tall man while I was playing football.
3. As he …………… (run), he fell down.
Answer: As he was running, he fell down.
4. The boy brought a letter and he ………. (still wait for your reply.
Answer: The boy brought a letter and he is still waiting for your reply.
Rule 17. Everyday (every month, every year), always, after, now-a-days आदि Present
Tense के सूचक हैं अतः इनके बाद Verb की I Form आयेगी। जैसे
1. I always ……….. (take) my breakfast at 7 a.m.
Answer: I always take my breakfast at 7 a.m.
2. One of my friends …………… (be) a doctor now-a-days.
Answer: One of my friends is a doctor nowadays.
Rule : 18 : यदि वाक्य के बीच में that हो (और ‘कि’ का अर्थ देता हो) तो that के पहले यदि Past
Tense हो तो that के बाद verb में प्रायः had + verb की III Form आती है। जैसे
1. Niru felt sure that she ……….. (hear) the voice of God.
Answer: Niru felt sure that she had heard the voice of God.
Forms Of Verbs
(With Golden Rules)
Three Forms :
Verb के तीन रूप (Three Forms) होते हैंI Form = Present Form II Form = Past Form III Form = Past Participle Past Participle का प्रयोग
(i) has, have, had के साथ होता है।
(ii) Passive Voice में होता है। विद्यार्थियों को प्रायः verb की Forms याद करने में कठिनाई होती है और उन्हें ये याद नहीं होती हैं। अतः लेखक ने इनके कुछ Golden Rules बनाए हैं, जिनसे सुविधा होगी।
Golden Rule : 1: जिस verb के बीच में – i हो तो प्रायः
(i) II Form में – 1 के स्थान पर – a लगा दो; तथा,
(ii) III Form में -1 के स्थान पर – u लगा दो, जैसे


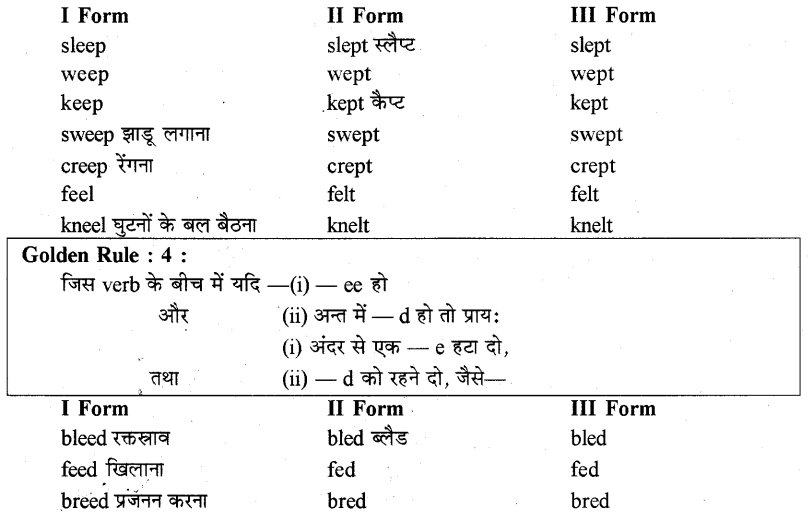











Practice Exercise 1:
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of verbs given in the brackets :
1. She…………..(take) exercises daily.
2. The sun…………… (set) in the west.
3. The chairman…………… (arrive) Jaipur next week.
4. India…………… (launch) her one more satellite.
5. India………….. (celebrate) her first Republic Day on 26 Jan. 1950.
6. Animals………….(love) their young ones…
7. We …………… (go) to school tomorrow.
8. His father ……… (meet) the principal yesterday.
9. When she opened the door, she……… (see) a terrible snake.
10. Our class teacher always ………….. (come) on time.
Answer:
1. takes
2. sets
3. will arrive
4. launches
5. celebrated
6. love
7. shall go
8. met
9. saw
10. comes
Practice Exercise 2.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of verbs given in the brackets with appropriate Simple Present, Past or Future Tense :
1. Fortune…………..(make) or mars a person.
2. Gravitational force…………(pull) everything towards it.
3. God………….. (help) those who help themselves.
4. A rotten apple…………… (smell) foul.
5. She…………… (think) she is right.
6. Everybody………….. (desire) worldly possessions.
7. She. ……………(appear) to be an officer.
8. The train had left the platform before I ……….. (reach) the station.
9. ………….. (not waste) your time, it is very important.
10. Margie ………… (go) to Delhi tomorrow to see her mother.
Answer:
1. makes
2. pulls
3. helps
4. smells
5. thinks
6. desires
7. appears
8. reached
9. Do not waste
10. will go
Practice Exercise 3:
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the Simple Present form of the verb :
1. We…………. (not live) without food.
2. Wheat………….(not heat) our stomach.
3. This jug…………..(contain) whey.
4. Flowers…………..(bloom) in spring season.
5. Ice…………… (melt) when it is heated.
6. Water………….. (freeze) at 0° celcius.
7. ……… You………….. (like) an apple a day?
8. …………..(not close) your eyes to the facts.
9. He usually……………(sit) in the front row.
10. She rarely……………(carry) an umbrella.
Answer:
1. do not live
2. does not heat
3. contains
4. bloom
5. melts
6. freezes
7. Do, like
8. Do not close
9. sits
10. carries
Practice Exercise 4.
Put the verbs in brackets into the correct Simple Present, Past or Future Tense :
1. The city buses…………… (run) along this street everyday.
2. I always…………….(spend) my holiday at a hill station.
3. My mother generally…………… (cook) breakfast after 8 o’clock.
4. We always…………..(enjoy) our Mathematics class.
5. My sister was crossing the road when she ………….. (fall) down and hurt her knee.
6. The driver pushed the brake and the bus …………….. . (stop)
7. We ……………. (do) it tomorrow.
8. He generally…………… (go) to the office with me.
9. Our class teacher usually………….. (wear) a Dhoti and a Kurta.
10. He usually…………… (get up) early in the morning
Answer:
1. run
2. spend
3. cooks
4. enjoy
5. feel
6. stopped
7. shall do
8. goes
9. wears
10. gets up
Practice Exercise 5.
Fill in the blanks with correct form of verbs given in brackets with Simple Present, Past or Future Tense :
1. Margie even……………(write) about it that night in her diary.
2. When he……………(be) a little boy his grandfather had told about it.
3. A vegetarian is the person who never…………… (eat) meat.
4. If it…………… (rain), all will be happy.
5. If the soldiers…………..(fight), they will win the battle.
6. He ………… (feel) sorry when he hears this news.
7. His mouth…………..(water) for the burfi that was his favourite sweet.
8. Tomorrow I ……….. (give) you some money so that you can buy your books.
9. Don’t be afraid of examination. I am sure you ……….(pass)
10. You can’t tell what the fools …………… (do) to you next.
Answer:
1. wrote
2. was
3. eats
4. rains
5. fight
6. will feel.
7. watered
8. shall give
9. will pass
10. will do
Practice Exercise 6.
Fill in the blanks with correct form of verbs given in brackets with appropriate Simple Present, Past or Future Tense :
1. Let’s hope we …………….. (meet) again.
2. It’s raining. If you go out you …………… (get) wet.
3. When I was young, I ………………. (want) to be a doctor.
4. The river Ganga …………..(flow) into the Bay of Bengal.
5. I don’t think he ……….. (come) to the party now.
6. Today’s arithmetic lesson …………. (be) on the addition of proper fractions.
7. I …. (buy) this scooter last month.
8. She always ……………. (remember) to send me a gift on my birthday.
9. I don’t want to go alone……………. you …………. (come) with me ?
10. I was thirsty, so I ……….. (drink) water quickly.
Answer:
1. shall meet
2. will get
3. wanted
4. flows
5. will come
6. is
7. bought
8. remembers
9. will, come
10. drank